Bijal Shah |
The recent expansion of Pell Grants to include short-term programs between eight and 15 weeks — under what’s known as Workforce Pell — marks a major legislative win for hundreds of thousands of students across the country and the institutions that serve them.
At its core, Workforce Pell has the potential to do three things: expand opportunity for entry-level and low-income Americans historically underserved by higher education opportunities; help employers close critical skill gaps in sectors like healthcare and manufacturing; and become a lever for economic resilience and national competitiveness in a rapidly evolving global landscape.
But realizing these benefits will take time, and with the federal policy scheduled to launch next summer, the practical work for policymakers now is how to drive the highest program persistence, job placement, and wage gains possible for America’s learners.
Against that backdrop, we offer the following perspectives grounded in Guild’s proprietary data on learner outcomes and performance across the programs in Guild’s learning marketplace. This article highlights what successful short-form programs can look like in practice, where potential trade-offs exist, and what policymakers might consider as they begin implementation later this year. This analysis is not meant to serve as an exhaustive account of every short-form learning program currently available in the U.S. learning market — or even Guild’s learning marketplace, but rather to provide unique market insights and best practices to inform the implementation process.
Short-form learning today
Today, Guild’s marketplace includes more than 1,000 programs that can be completed in 12 months or less. Of these, nearly half are designed to be completed in 16 weeks or less — a format increasingly aligned with the needs of time-constrained, working learners. To date, approximately 137,000 learners have enrolled in short-form programs on Guild’s platform, including more than 84,000 in programs under four months in length. Importantly, all Guild learners are working and the vast majority are over the age of 25, with 41% reporting working 40+ hours per week while enrolled.
Quality and eligibility under Workforce Pell
OBBBA sets forth the following criteria to qualify for Workforce Pell.
Run between 8 to 15 weeks and comprise 150 to 599 clock hours;
Are delivered by accredited institutions and have been offered for at least (1) year;
Align with high-demand roles and culminate in recognized, portable credentials;
Achieve completion and job-placement rates of at least 70%; and
Are provided at total tuition and fees below the median value-added earnings of graduates, defined as earnings at least 150% above the federal poverty line.
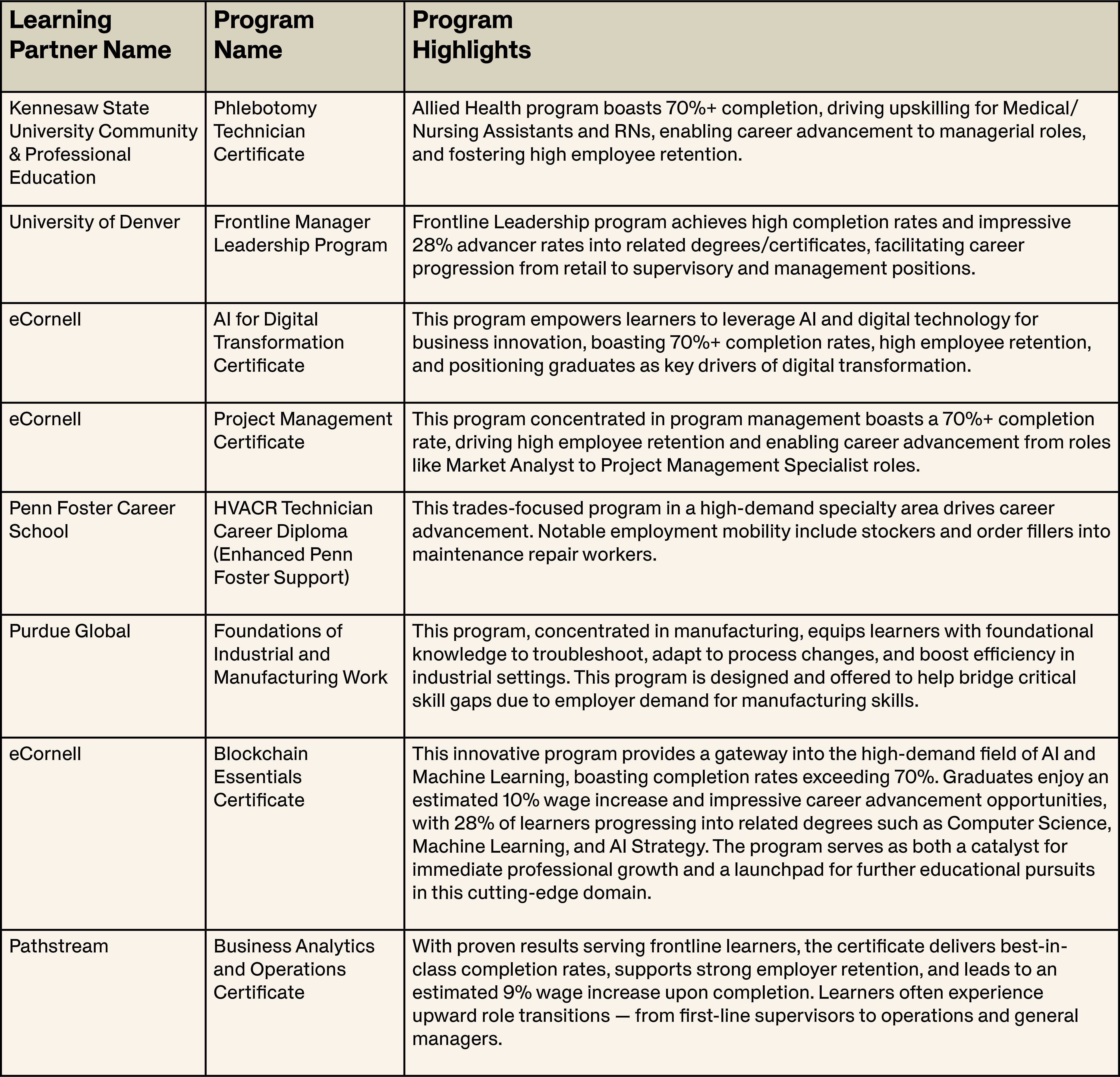
Using program-level provider data alongside employer outcomes data, we have identified a number of programs within our learning marketplace that demonstrate these criteria — particularly around duration, quality, affordability, and workforce relevance — and are aligned with the goals and qualifications for Workforce Pell. What follows is a sampling of those programs that reflect the diversity of industry sectors, formats, and outcomes that short-form learning can support, especially when designed with working adults in mind. While not all of these programs may ultimately qualify for Workforce Pell, they all demonstrate its spirit: enabling economic mobility through affordable, career-relevant education.
A snapshot of short-form programs to consider
MedCerts
Phlebotomy Technician certificate
In the healthcare sector, MedCerts’ Phlebotomy Technician Certificate stands out for its combination of high completion rates, role mobility, and credit transferability through established partnerships with accredited institutions. The program attracts a broad range of learners across the allied health spectrum and supports occupational transitions such as from Nursing Assistants or Home Health Aides to Phlebotomists, as well as upskilling opportunities for Clinical Laboratory Technicians and Medical Assistants. The certificate can also be applied toward two- or four-year degrees via MedCerts’ academic partnerships. With strong labor market alignment and mobility metrics, this program meets the spirit and substance of Workforce Pell’s goals: to fund short-term training that leads directly to in-demand, better-paying roles.
MedCerts
IT Security and Network Technician (CompTIA Net+ & Sec+)
Also from MedCerts, the IT Security and Network Technician program equips frontline workers with the technical skills needed to transition into high-demand cybersecurity and network administration roles. Preparing learners for the CompTIA Network+ and Security+ certifications — widely recognized in the IT industry — the program meets Workforce Pell’s completion threshold. Participants see an average wage increase of 8% within one year of enrollment, underscoring the economic value of tech-aligned short-form credentials. As the U.S. economy increasingly depends on digital infrastructure, this program demonstrates how Pell-funded upskilling can close critical gaps in the technical labor force.
Bellevue University
People & Business Leadership certificate
Bellevue’s People & Business Leadership Certificate exemplifies the kind of short-form, stackable credential Workforce Pell is intended to support. Focused on career fundamentals and skill-building in areas critical for emerging managers and leaders at an enterprise, the program is highly relevant to frontline workers and integrates seamlessly with Bellevue’s business degree pathways. The certificate has strong completion rate outcomes that meets the 70% threshold set by Workforce Pell, and the program also boasts a 31% “advancer” rate (defined as learners who move on to further degrees or certifications). Importantly, the program also drives measurable career mobility. Many participants transition from retail sales into supervisory roles, reflecting substantial economic advancement. Guild observes that learners in this program experience an estimated 12% average wage increase within one year. Bellevue’s reputation as a learning provider for working adults further strengthens this offering’s credentials as a high-impact, low-barrier solution for workforce development.
Rio Salado College
Certificate of Completion in Introduction to Semiconductor Manufacturing
This program provides a comprehensive training experience tailored to upskill learners for in-demand manufacturing roles. Offered by one of our community college partners with a strong track record of serving working adult learners, Rio Salado’s program delivers significant value to both employers and learners in the growing semiconductor industry. Importantly, this certificate is designed to meet local workforce needs in the Maricopa region that Rio Salado serves, and reflects the spirit of the principles outlined in the Workforce Pell legislation — connecting learners with foundational knowledge and hands-on skills aligned to regional job opportunities. Graduates are equipped for roles such as Process Technicians, Equipment Technicians, and Quality Control Specialists.
Springboard
Machine Learning for Engineers certificate
Springboard’s Machine Learning bootcamp has demonstrated stellar completion rates (~85%), unlocking advanced upskilling. Enrolled learners tend to already be in related roles, and show some of the highest employee retention rates among the programs Guild evaluated. Programs like this can help employers develop the skills needed in a rapidly evolving technology landscape within their existing workforce, preventing displacement.
SisuCare Education
Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) Training Program
SisuCare’s Certified Nursing Assistant Training Program offers a flexible, hybrid learning experience tailored to working adults in the healthcare sector. Its high completion rates, and employee retention figures point to exceptional value. Many learners transition from service-sector roles — such as customer service or sales — into high-demand CNA roles.
eCornell
Python for Data Science certificate
eCornell’s Python for Data Science program is a rigorous, longer-form certificate that addresses the growing demand for analytics and data fluency across sectors. The program’s outcomes suggest a strong return on investment: learners demonstrate mobility from technical roles (e.g., database administrators) to software development or operations leadership. As AI and data literacy become foundational to 21st-century work, Workforce Pell should consider expanding to include programs that equip learners with these advanced capabilities.
Chegg Skills
Applying AI in Customer Service certificate
Chegg Skills' Applying AI in Customer Service Certificate is a cutting-edge program designed to teach the AI skills needed to enhance modern customer service roles. With completion rates above 70%, this offering demonstrates strong learner engagement and outcomes. It provides significant value by enabling learners to harness the power of AI to enhance efficiency, personalize interactions, and deliver superior service. Occupations that benefit from this program include a wide array of frontline and managerial roles focused on enhancing the customer experience such as Compensation and Benefits Managers, Tellers, Financial Specialists, and other roles.
While role mobility is a critical outcome, it doesn’t capture the full return on short-form learning. In our dataset, roughly one in four learners moves into a new role within 12 months of enrollment, and mobility rises further over time. For those who stay in-role during that first year, upskilling is often the measurable payoff: new skills, greater confidence, and higher productivity that lift team performance and set up later advancement. Findings from a recent Guild survey of 1,000 learners reinforce this pattern, showing gains in on-the-job performance and manager-reported impact within months of enrollment. Taken together, the evidence suggests that benefits begin before a title changes—and that upskilling can be a purposeful, value-creating outcome.
Success factors of short-form learning
Our experience delivering short-form learning at scale reveals several consistent factors that drive stronger outcomes — particularly for working adults balancing full-time jobs, caregiving responsibilities, and financial pressures. With more than 100,000 learners enrolled in short-form programs through our platform, Guild has developed a nuanced understanding of what works, for whom, and why. This section distills that insight into a high-level analysis of program design features that matter most for learner persistence, completion, and mobility. From this data, clear patterns emerge — each with important implications for the effective implementation of short-form learning and Workforce Pell:
Time commitment for learning programs matters, especially for working adults.
Learning programs under 16 weeks consistently show higher completion rates than longer ones. However, for Guild learners who often balance full-time jobs and caregiving responsibilities, both duration and a manageable weekly workload are critical factors for success. In fact, our data shows that for each hour added of weekly instruction, the odds of completion decline. Properly calibrated programs that are mindful of the time commitment required each week are best suited for enabling working adults to complete their learning journey. Striking the right balance between program duration and weekly time commitment is essential to optimize completion rates for this demographic.
Programs that are career-aligned drive higher completion.
For working adults, programs that have strong career alignment and that have a defined job to be hired into yield higher rates of educational success. Guild data shows that this integration of professional goals and content mastery, increases engagement and motivation.
Internal mobility is a high-value outcome that is often overlooked in traditional policy frameworks.
For many learners, the goal is not to leave their current employer but to stay and move up or laterally. Promotions, title changes, and expanded job scopes all reflect meaningful workforce gains, particularly in sectors like healthcare, logistics, and retail where external hiring pipelines may be limited. Internal mobility is also one of the strongest signals of business alignment.
‘Wraparound’ services matter.
Guild defines these as coaching and career-navigation support, and they are strongly correlated with both learner persistence and satisfaction. There are 23 more completions for every 100 short form learners who work directly with Guild Coaching, signaling higher engagement and stronger support in fast-paced, work-aligned environments. These services help learners set goals, navigate challenges, and connect effort to outcomes. When they’re present, learners are more likely to finish, apply what they’ve learned, and stay with their employer.
Considerations for policymakers
Guild fully supports the primary goal of Workforce Pell: to expand access to high-quality, career-relevant learning for working adults. As implementation begins, we offer the following broad recommendations:
Explore a time-limited pilot authority to test experimental pathways. For programs that fall outside statutory definitions (e.g., just under 150 clock hours or just over 15 weeks), a pilot would be helpful to the Department in gathering comparative outcomes data. This data could inform future decisions on what quality and completion look like across diverse learner populations.
Broaden definitions of success to include ‘internal mobility’. When defining quality, consider including guidance to explicitly recognize role change, pay increase, or title progression within a learner’s current employer as valid indicators of workforce outcome success under the “related employment” standard.
Clarify alignment expectations between programs and labor market needs. Provide examples of how career alignment may be demonstrated beyond Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data, such as employer endorsement, industry certification preparation, or wage progression tied to program completion.
Require outcome transparency. In implementation guidance, reporting on completion rates, employment outcomes (including internal role changes), and learner satisfaction — broken out by learner type and program format — is critical.
Turning policy into outcomes
We believe Workforce Pell represents a major step toward aligning federal financial aid with the needs of today’s learners and labor market. Successful implementation will be critical, especially how quality is defined and measured. Guild’s data shows that short-form programs can deliver real impact when they’re designed with the learner in mind and supported by a strong, supportive infrastructure. As implementation begins, we look forward to supporting policymakers, employers, and providers in building a system that delivers on the promise of equitable, career-relevant education for all.